There are various race series, and If the racing car changed, the race distance and how to decide the champion would also change. Although there are many complicated and difficult regulations, it explains basic knowledge about motorsport.
The type of racing car
Racing cars in automobiles can be mainly classified into the following three types.
- Formula car
- Prototype car
- Touring car
Formula car
The Formula Car is a racing car that conforms to the standard of open wheels represented by Formula 1. Each country has its own evolution, such as SUPER FORMULA in Japan and Indycar series in the United States.
Recently, Formula E which uses an EV formula car that runs on the motor instead of the engine, has been added as a new series.

Representative categories
Europe
Formula 1, Formula 2, Formula 3, Formula E
USA
NTT IndyCar Series, Indy Lights
Japan
SUPER FORMULA, SUPER FORMULA LIGHTS, Formula Regional、FIA-F4、JAF-F4、Super FJ
Prototype car
Prototype car is represented by the WEC (World Endurance Championship) and, unlike formula car, is characterized by a cowl-covered wheels. On the body design, it has various shapes such as closed type (with roof) and open type (without roof). Le Mans 24 hours endurance race, which is one race of the WEC series, is particularly famous.

Representative categories
Europe
WEC, European LeMans Series
USA
American LeMans Series
Asia
Asian LeMans Series
Touring car
Touring Car is a car based on a passenger car and modified to a racing car. In Japan, SUPER GT series and Super Taikyu series are famous. One-make races using TOYOTA 86, SUBARU BRZ and TOYOTA Vitz are also held in various places.

Representative categories
Europe
WTCR, DTM, Blancpain GT Series, 24 Hours Nürburgring
USA
NASCAR
Japan
SUPER GT, Super Taikyu, TOYOTA Gazoo Racing 86/BRZ Race
Type of race session
The sessions of motorsports are mainly classified into the following three sessions.
- Free practice
- Qualifying
- Race
In the free practice and the qualifying session, the drivers are ranked according to the lap time of one lap. In the race, the drivers are ranked according to the order at the control line after completing the predetermined number of laps.
Free practice
During the free practice, it is specified the start time and end time, the driver can drive the racing car freely within the time. The team and driver set up the car according to each circuit and the weather at the time. But it is used for various purposes such as getting used to the circuit and knowing the characteristics of tires.
The ranking is determined according the order of the best lap time, but the result of the free practice is not recorded, so some team evaluates the lap time for the qualifying session, some team evaluate the lap time on long distance for the race. Therefore, it is impossible to judge whether it is fast or slow just by the lap time in free practice.
Qualifying
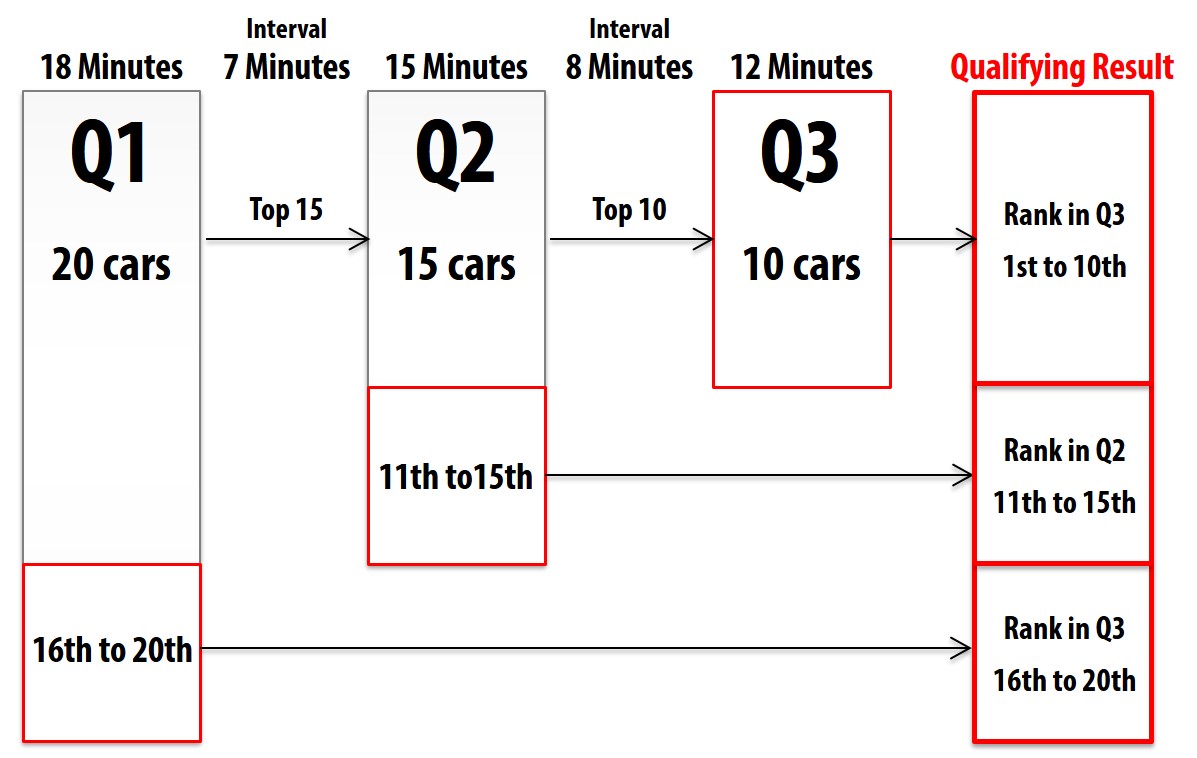
In the qualifying session, the starting order of the race is decided. The driver performs time attack, and the ranking is competed by the lap time. Previously, like the free practice, the start time and end time were set. The driver performed time attack within the time, and ranking was competed. At present, in the mainstream method such as Formula 1, multiple short sessions called Q1, Q2 and Q3 are conducted. In each session, the driver performs time attack, and the ranking is determined from the grid behind.
The flow of the qualifying session on Formula 1
In the qualifying session of Formula 1, the session is consisted of three sessions, Q1, Q2 and Q3. If the number of the cars is 20 or more, at first Q1 that is 18 minutes is take place, all drivers perform a time attack, and the five slowest cars are ranked (16th to 20th). The top 15 cars advances to Q2 and the lap time recorded in Q1 is deleted.
There is a 7-minute interval after the Q1, and Q2 that is 15 minutes is take place. The driver performs a time attack in the same way as in Q1, and the five slowest cars (11th to 15th) is ranked. The top 10 cars advances to Q3 and the lap time recorded in Q2 is deleted.
There is an 8-minute interval after the Q2, and Q3 that is 12 minutes is take place to determine the ranking of the remaining 10 cars (1st to 10th).
The cars stopped on the course during the qualifying session are not be able to run in further sessions.
Race
In the race, starting from the grid order determined by the qualifying session, the ranking is determined in the order of crossing the control line after completing the predetermined the number of laps.
When the same lap time is recorded
If more than one driver records the same lap time in the qualifying session, the driver that recorded earlier is ranked higher.
If multiple cars cross the control line at the same time in the race and finish, the ranking is determined by photo judgement.
Race format on the race
The race format is mainly classified into the following two types.
- Running the predetermined the number of laps
- Running for the predetermined race time
Running the predetermined the number of laps
The number of race laps is determined in advance, as represented by races such as Formula 1, SUPER FORMULA, and SUPER GT. The race distance is determined by the regulations of the series, so the number of laps is determined according to the distance of each circuit. When the predetermined lap is completed, chequered flag is waved from the top of the car at the observation post near the control line, and the race ends.
Even if it could not compelete the race (even if it could not receive the chequered flag), if it competes the predetermined the number of laps by regulations, it is treated as compeleted the race.
Even though the race distance is determined by the number of laps, the end of the race is determined by the maximum time. In Formula 1, even if it have not completed the determined the number of laps, the lap 2 hours after the race start becomes the last lap. This is called the “two hours rule” and is well known in Formula 1.
Race distance example
Formula 1
Minimum number of laps over 305 km
SUPER GT
First lap over 250 – 1000km
SUPER FORMULA
110 – 300km
5) CHAMPIONSHIP EVENTS
5.1 Events are reserved for Formula One cars as defined in the Technical Regulations.
5.2 Each Event will have the status of an international restricted competition.
5.3 The distance of all races, from the start signal referred to in Article 36.9 to the end-of-race signal referred to in Article 43.1, shall be equal to the least number of complete laps which exceed a distance of 305km. However, should two hours’ elapse before the scheduled race distance is completed, the leader will be shown the end-of-race signal when he crosses the control line (the Line) at the end of the lap following the lap during which the two hour period ended, provided this does not result in the scheduled number of laps being exceeded. Only under the circumstances below will any exception be made to the above :
a) The distance of the race in Monaco shall be equal to the least number of complete laps which exceed a distance of 260km.
b) Should the race be suspended (see Article 41) the length of the suspension will be added to this period up to a maximum total race time of four hours.
c) If the formation lap is started behind the safety car (see Article 36.14(c)) the number of race laps will be reduced by the number of laps carried out by the safety car minus one.
Running for the predetermined race time
This format is represented by race series such as WEC and Super Taikyu, and is mainly used in endurance races. Race time is not standardized, but is determined for each race series, and WEC and Le Mans 24 hours Endurance Race are particularly famous.
The lap that has went the specified time is the last lap, and at the end of this lap, chequered flag is waved from the top car. It is not often determined the number of laps on races defined by time, in which case, unless the chequered flag is received, it is not treated as completing the race.
Race distance example
WEC
6 hours minimum
How to decide the champion
In race series where races are held on multiple circuits such as Formula 1 and SUPER GT, points is awarded to drivers and teams according to the result of each race, and it is competed based on the number of points throughout the year. The driver and team with the most points become the series champion.
The points earned for each race vary from series to series and defined in the supplementary regulations for each series. In Formula 1, the following points is awarded from 1st to 10th.
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 6th | 7th | 8th | 9th | 10th |
| 25 | 18 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
In Formula 1, the title is given not only to the driver but also to the constructor (team). Since two drivers are participating from the one team, the total points earned by the two drivers are added as constructors points.
In the case a tie on the same points, the driver who the number of win is higher is ranked higher. If both drivers have the same number of wins, the driver who the number of second place is higher is ranked higher. If it cannot still decide, The driver who the number of third place, fourth place … is higher is ranked higher. If it cannot still decide, the race steward may decide the champion.
Depending on the race series, points may be awarded to drivers who have won the pole position in the qualifying session or who have recorded the fastest lap in the race.
6) WORLD CHAMPIONSHIP
6.1 The Formula One World Championship driver’s title will be awarded to the driver who has scored the highest number of points, taking into consideration all the results obtained during the Events which have actually taken place.
6.2 The title of Formula One World Champion Constructor will be awarded to the competitor which has scored the highest number of points, results from both cars (see Article 8.6) being taken into account.
6.3 A constructor is the person (including any corporate or unincorporated body) which designs the Listed Parts set out in Appendix 6. The make of an engine or chassis is the name attributed to it by its constructor.
The obligation to design and use Listed Parts shall not prevent a constructor from outsourcing the design and/or manufacture of any Listed Parts to a third party in accordance with the provisions of Appendix 6.
If the make of the chassis is not the same as that of the engine, the title will be awarded to the former which shall always precede the latter in the name of the car.
6.4 Points for both titles will be awarded at each Event according to the following scale :
1st : 25 points
2nd : 18 points
3rd : 15 points
4th : 12 points
5th : 10 points
6th : 8 points
7th : 6 points
8th : 4 points
9th : 2 points
10th : 1 point
In addition to the above, one point will be awarded to the driver who achieved the fastest valid lap time of the race and to the constructor whose car he was driving, provided he was in the top ten positions of the final race classification (see Article 45). No point will be awarded if the fastest valid lap time is achieved by a driver who was classified outside the top ten positions.
6.5 If a race is suspended under Article 41, and cannot be resumed, no points will be awarded if the leader has completed two laps or less, half points will be awarded if the leader has completed more than two laps but less than 75% of the original race distance and full points will be awarded if the leader has completed 75% or more of the original race distance.
If the formation lap is started behind the safety car (see Article 36.14(c)), the original race distance will be deemed to be the distance calculated in accordance with Article 5.3(c).
However, the maximum race time of four hours (see Article 5.3(b) will commence at the scheduled race start time.
6.6 The drivers finishing first, second and third in the Championship must be present at the annual FIA Prize Giving ceremony.
7) DEAD HEAT
7.1 Prizes and points awarded for all the positions of competitors who tie, will be added together and shared equally.
7.2 If two or more constructors or drivers finish the season with the same number of points, the higher place in the Championship (in either case) shall be awarded to :
a) The holder of the greatest number of first places.
b) If the number of first places is the same, the holder of the greatest number of second places.
c) If the number of second places is the same, the holder of the greatest number of third places and so on until a winner emerges.
d) If this procedure fails to produce a result, the FIA will nominate the winner according to such criteria as it thinks fit.























33) QUALIFYING PRACTICE
33.1 The qualifying practice session will take place on the day before the race and will start no less than two hours after the end of P3.
The session will be run as follows :
a) For the first eighteen minutes of the session (Q1) all cars will be permitted on the track and at the end of this period the slowest five cars will be prohibited from taking any further part in the session.
Lap times achieved by the fifteen remaining cars will then be deleted.
b) After a seven-minute break the session will resume for fifteen minutes (Q2) and the fifteen remaining cars will be permitted on the track. At the end of this period the slowest five cars will be prohibited from taking any further part in the session.
Lap times achieved by the ten remaining cars will then be deleted.
c) After an eight-minute break the session will resume for twelve minutes (Q3) and the ten remaining cars will be permitted on the track.