Blue flag is displayed to cars that are about to be overtaken by faster cars from behind.
In the race the driver who is about to be lapped down will be waved.
The display of blue flag is performed by waving.
Regulations
CHAPTER IV - CODE OF DRIVING CONDUCT ON CIRCUITS
2. Overtaking, car control and track limits
a) A car alone on the track may use the full width of the said track, however, as soon as it is caught by a car which is about to lap it the driver must allow the faster driver past at the first possible opportunity.
If the driver who has been caught does not seem to make full use of the rear-view mirrors, flag marshals will display the waved blue flag to indicate that the faster driver wants to overtake.
Any driver who appears to ignore the blue flags will be reported to the Stewards.
Operation during the free practice and the qualifying session
Blue flag notifies driver of faster car is approaching from behind.
It is basically waved to alert the driver. However, if it is judged that the driver has unduly interfered with other driver, Penalties may be imposed.
Particularly during qualifying session, it is highly likely that a penalty will be imposed in case a non-time-attacked car is waved with blue flag but obstructs the time-attacked car without giving way.
During time attack, in case a faster car is approaching from behind a slow car and blue flag is waved against the slow car, the slow car is not obstructing. In this case there is very little possibility of a penalty.
Blue flag is waved by the next observation post of the car where a faster car is approaching from behind.
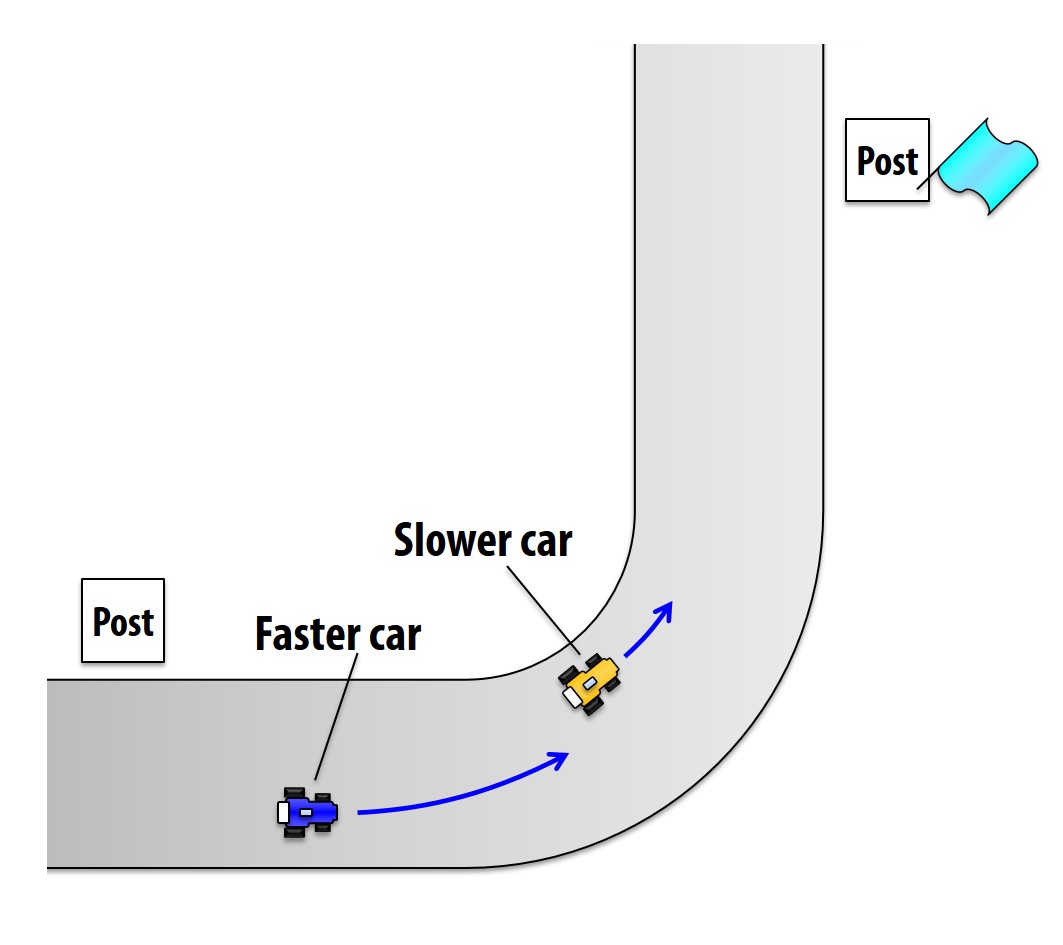
Operation the during race
In the race, blue flag is waved for the driver who is lapped down. Unlike the free practice and qualifying session , the driver who is waved the blue flag must let the following car go ahead.
In case the driver who is waved bule flag does not let the following car go ahead, it may be imposed the penalty.
Formula 1 sets guidelines that it must be let the following car go ahead within 3 observation post sections after the blue flag is waved.
In the race, blue flag will be waved to car that is about to be lapped down.
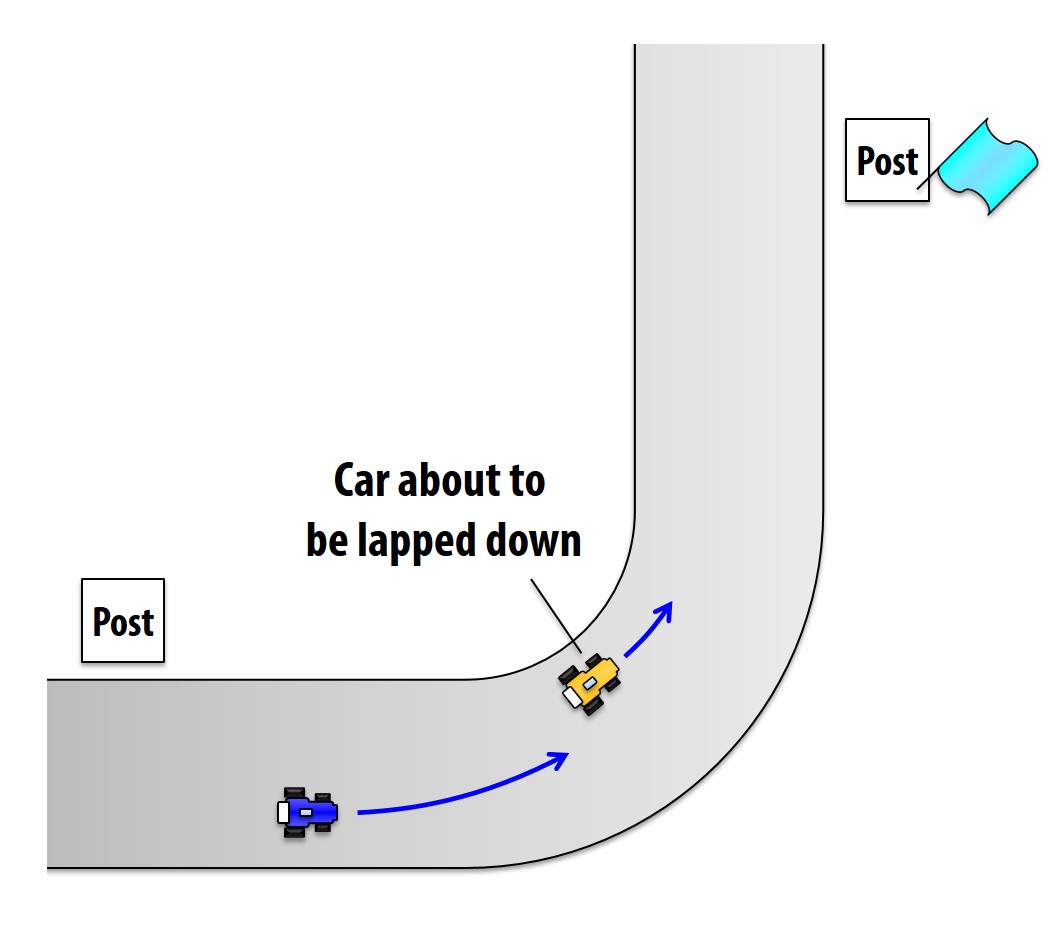
In races with large speed differences due to class difference such as Super Taikyu, blue flag may be waved when a faster car is approaching from behind, regardless of whether it is lapped down or not.
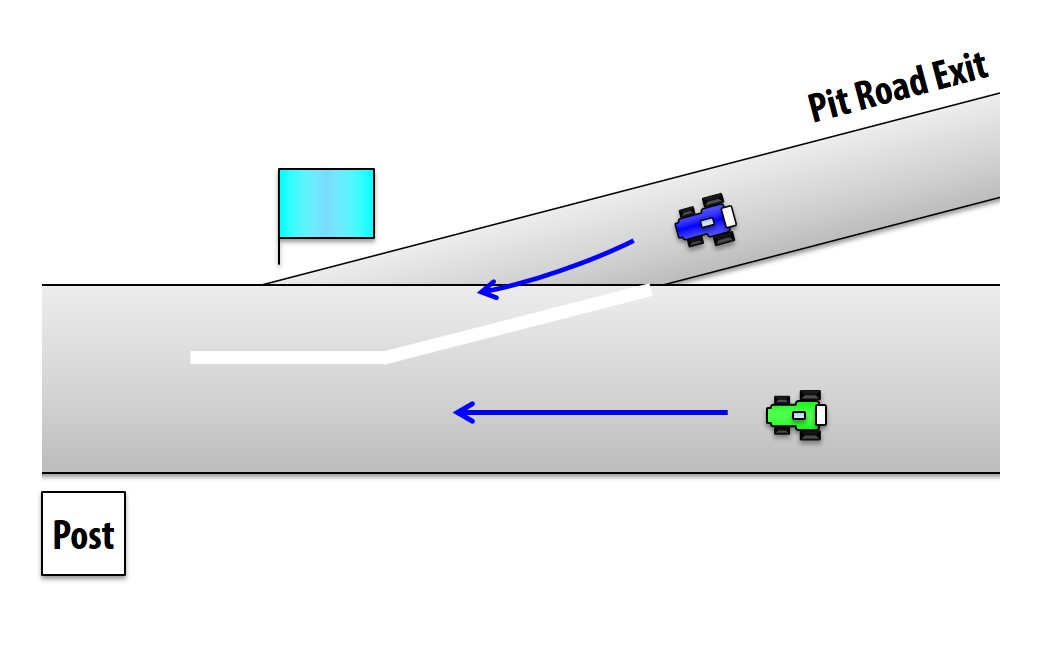
Operation at pit load exit
If the car running on the main straight and the car going out of the pit are likely to intersect, blue flag will be displayed statically to the car going out of the pit near the pit road exit.
If the pit-out car enters the course so as to block the car running on the main straight, it may be penalized.
When the pit-out car and the car running on the main straight are likely to intersect, blue flag is displayed near the pit road exit.

出典:youtube.com
The most difficult to wave the blue flag
Waving the blue flag is the most difficult among course marshalls. Because the driver’s line of sight is always far in the direction of travel, the blue flag must be waved long before passing the front of observation post.
Therefore, during qualifying session, it is necessary to always know the locations of cars that are time attacking and those that are not.
During the race, it is necessary to know the location of the car that is lapped down.
In addition, it is necessary to judge the distance between cars and the speed difference in an instant, and to wave the blue flag.























2.5.5.1 d) Blue flag
This should normally be waved, as an indication to a driver that he is about to be overtaken. It has different meanings during practice and the race.
At all times:
– A stationary flag should be displayed to a driver leaving the pits if traffic is approaching on the track.
During practice:
– A faster car is close behind you and is about to overtake you.
During the race:
The flag should normally be shown to a car about to be lapped, if the driver does not seem to be making full use of his rear-view mirrors.
When shown, the driver concerned must allow the following car to pass at the earliest opportunity.